All six major universities in Hong Kong have formed student teams to participate in the HKAES 2023-24 University Pitch Competition. Each team consists of 4 - 6 undergraduate students who are not in their final year of study, with at least half of the members being engineering or computer science students. Their individual profile can be found hereunder.
Thus, we are developing an AI-powered solution that leverages technology to empower vulnerable individuals by providing them with comprehensive information about their food intake and alerting them to potential risks based on their specific vulnerabilities. This solution aligns with the theme of "AI-empowered Solutions for Climate Change Challenges" and contributes to the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals.


Consequently, having accurate predictions of these disasters would be immensely beneficial for addressing the problems of lack of preparation for people living there when they are facing the catastrophe, especially in less developed countries.
In our project, we predict the occurrence of a weather-related catastrophe using weather data as input and catastrophe data as labels, including heat waves, and typhoons. After feeding the data to our model, the project can forecast some catastrophes in the near future based on the weather data and able to inform people to be prepared in advance.





To address these issues, we propose FarmGPT, an AI-based solution for farmers. Our project involves fine-tuning a chatbot with two types of information. Firstly, we utilize farming-related data, such as AFCD reports, to ensure the model provides accurate information. Secondly, we input farm-specific information obtained through sensors and cameras to generate tailored recommendations that minimize the impact of these challenges.
FarmGPT has a twofold impact.
Firstly, it empowers farmers by providing dynamic AI analysis of their farmland, bridging the technology gap through conversational and digestible information.
Secondly, it enables precision agriculture, allowing farmers to scale their operations while adapting to specific land needs. This approach reduces the reliance on destructive practices like tilling and nitrogen fertilizers, which contribute to climate change. By embracing precision agriculture, farmers can better adapt to the changing environment caused by climate change and mitigate its effects.



Presentation
Student Team Members
| Name | Study Program | Study Year |
| Sanskar SHRESTHA | Computer Science | 4 |
| KADESSOVA Ayazhan | Computer Science | 3 |
| UCHE Destiny Nnanna | Computer Science | 3 |
| Mohammad Riasad HUQ | Computer Science | 2 |
| ONG Jun Kye Eric | Computer Science | 3 |
InfoBite: Enhancing Food Awareness and
Nutritional Monitoring for Vulnerable Individuals
Thus, we are developing an AI-powered solution that leverages technology to empower vulnerable individuals by providing them with comprehensive information about their food intake and alerting them to potential risks based on their specific vulnerabilities. This solution aligns with the theme of "AI-empowered Solutions for Climate Change Challenges" and contributes to the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals.


Presentation
Student Team Members
| Name | Study Program | Study Year |
| LIU Xianlong Lambert | Computer Science | 2 |
| CHAN Lap Yan Lennon | Artificial Intelligence Science and Technology | 1 |
| Thapakorn PIPATPAJONG | Computational Data Science | 2 |
| WEI Chi Kong Thomas | Earth and Environmental Sciences | 2 |
Prediction of Natural Catastrophe using Artificial Intelligence
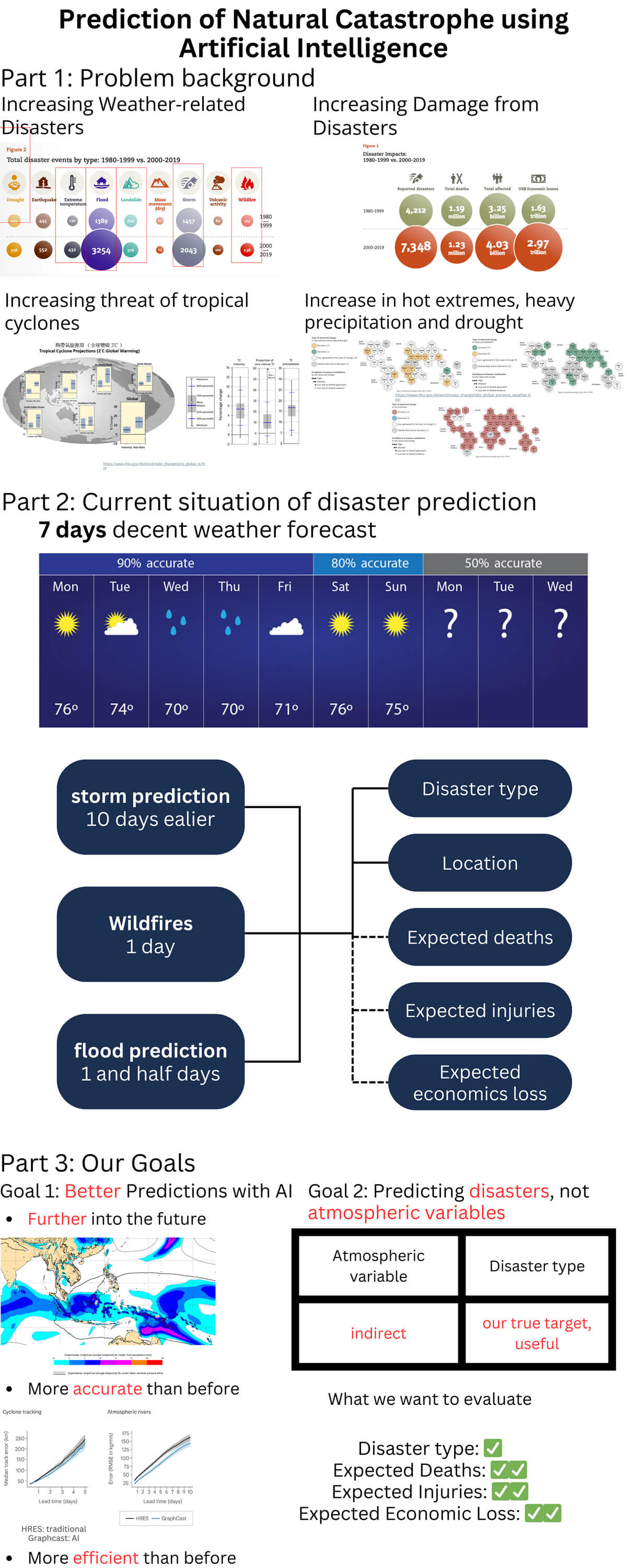
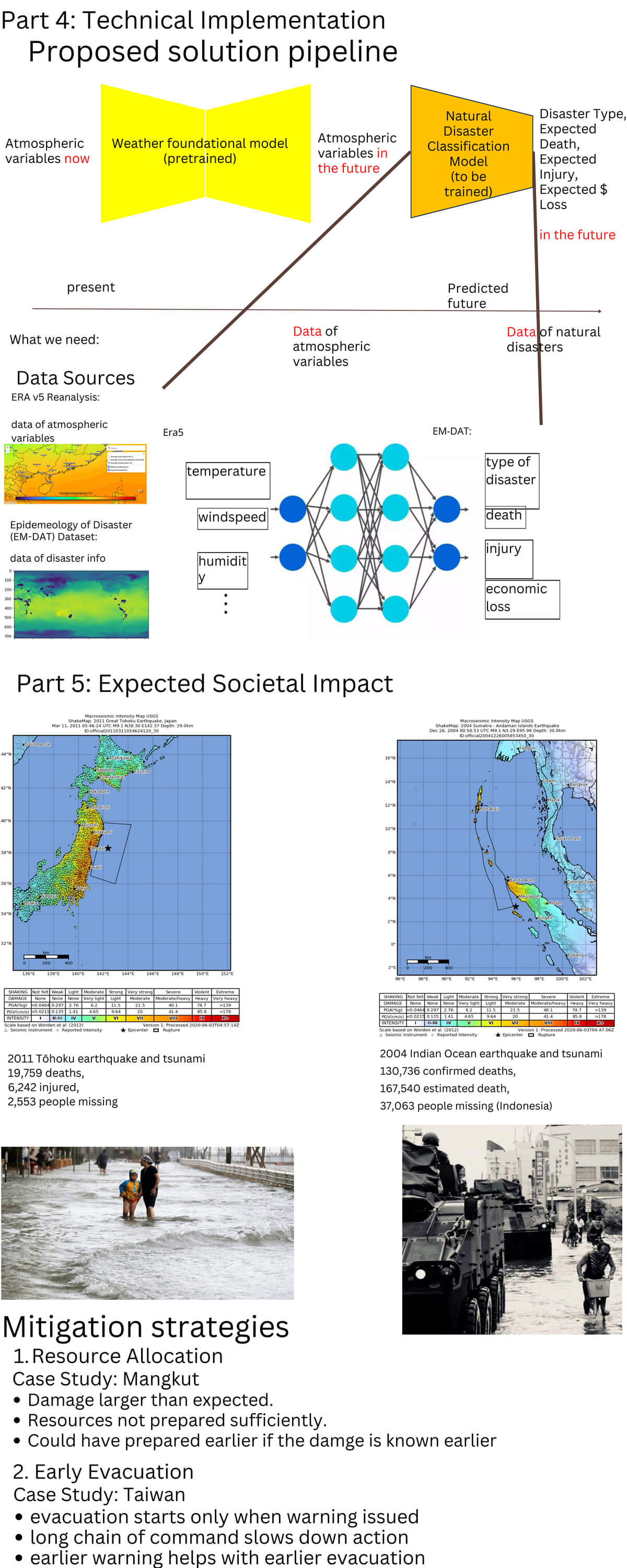
Natural catastrophes can cause loss of life and damage property. With the increasing severity of climate change, the frequency of disasters has significantly risen.Consequently, having accurate predictions of these disasters would be immensely beneficial for addressing the problems of lack of preparation for people living there when they are facing the catastrophe, especially in less developed countries.
In our project, we predict the occurrence of a weather-related catastrophe using weather data as input and catastrophe data as labels, including heat waves, and typhoons. After feeding the data to our model, the project can forecast some catastrophes in the near future based on the weather data and able to inform people to be prepared in advance.



Presentation
Student Team Members
| Name | Study Program | Study Year |
| GUO Aobo | Electrical Engineering | 2 |
| CHU Weiqi | Civil Engineering | 3 |
| Sanseong KWEON | Nuclear & Risk Engineering | 2 |
| Jason ALEXANDER | Civil Engineering | 3 |
| QUE Yue | Data Science | 3 |
AI-Assisted Smart Space Cooling Approach with Ultra-High Cooling Power
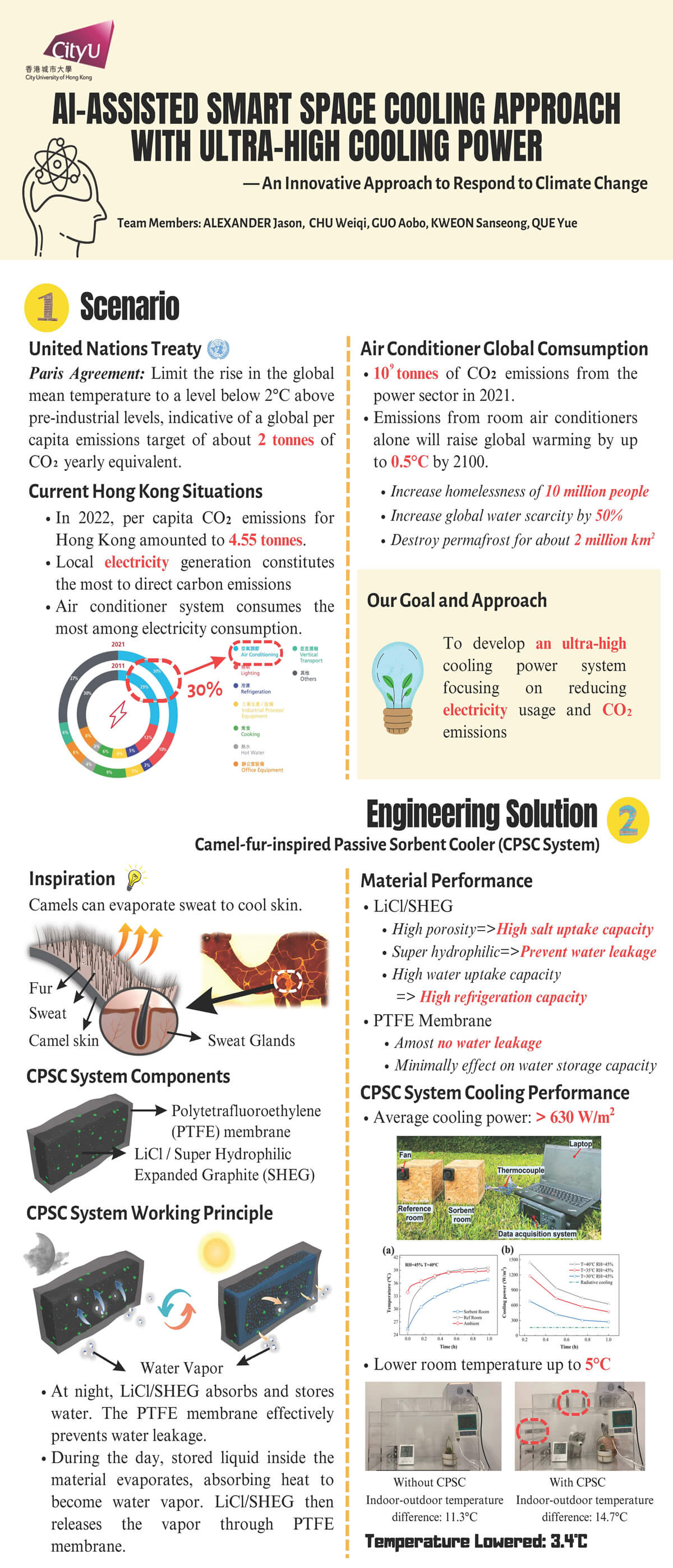
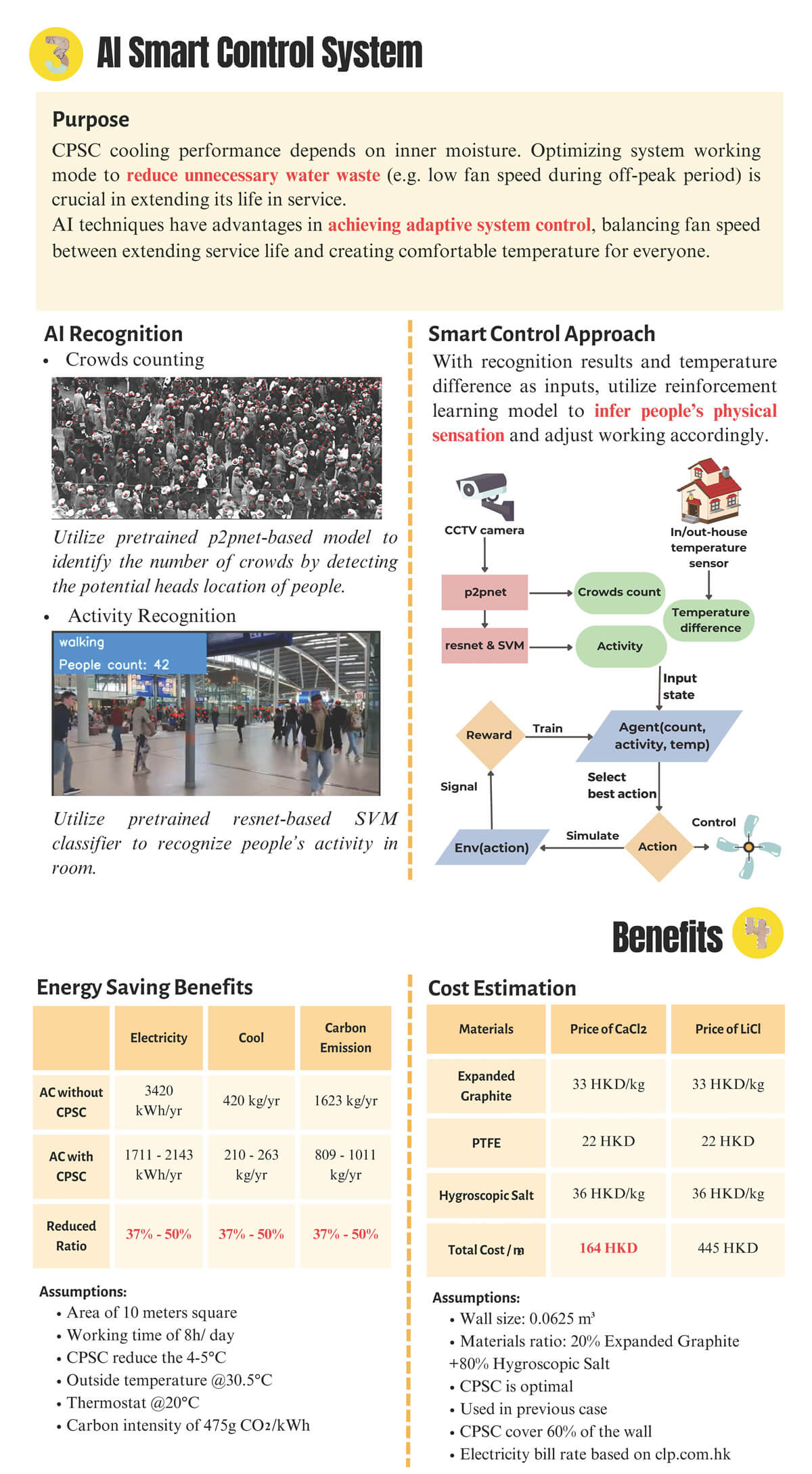
The increasing worldwide demand for cooling and electricity exacerbates the problem of global warming. Recent studies indicate that the increasing global adoption of air conditioners will triple the energy demand for space cooling without any action to address energy efficiency by 2050. Therefore, developing cooling technologies that operate with lower energy consumption is the research we investigate. Inspired by how camels adapt in the desert, we design a camel-fur-inspired sorbent that can periodically absorb the moisture from the air at night and release its stored water during the daytime for building cooling. The novel sorbent would circulate in response to the environment and exhibit outstanding cooling performance, which is almost 4 times the classical radiative-cooling approach. Concurrently, we propose an Artificial Intelligence (AI) integrated with ultra-high cooling power sorbent to achieve smart cooling in buildings. Highly effective cooling control can be managed by analysing user behaviour through AI.


Presentation
Student Team Members
| Name | Study Program | Study Year |
| PAL Ileana | Mechanical Engineering | 3 |
| DUAN Mingjie Josie | Land Surveying and Geo-informatics | 3 |
| WANG Zian Peter | Electronic and Information Engineering | 3 |
| GAMAGE Sashenka | Electronic and Information Engineering | 2 |
| WANG Youkang Albert | Computer Science | 2 |
| ZHANG Tianyi Tonax | Computer Science | 3 |
EcoFlight: Enhancing Aircraft Ground Operations for Reduced Carbon Emissions
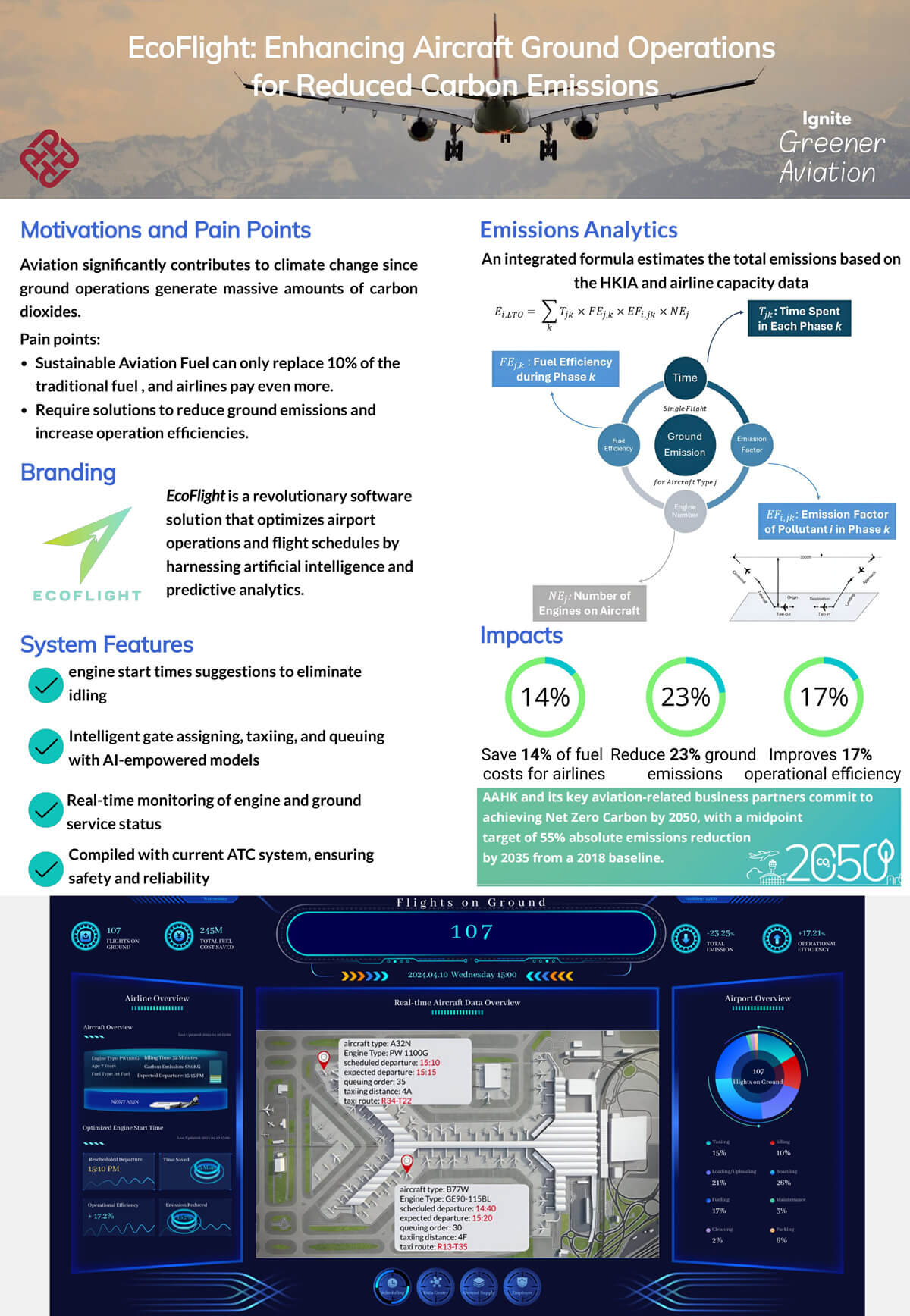
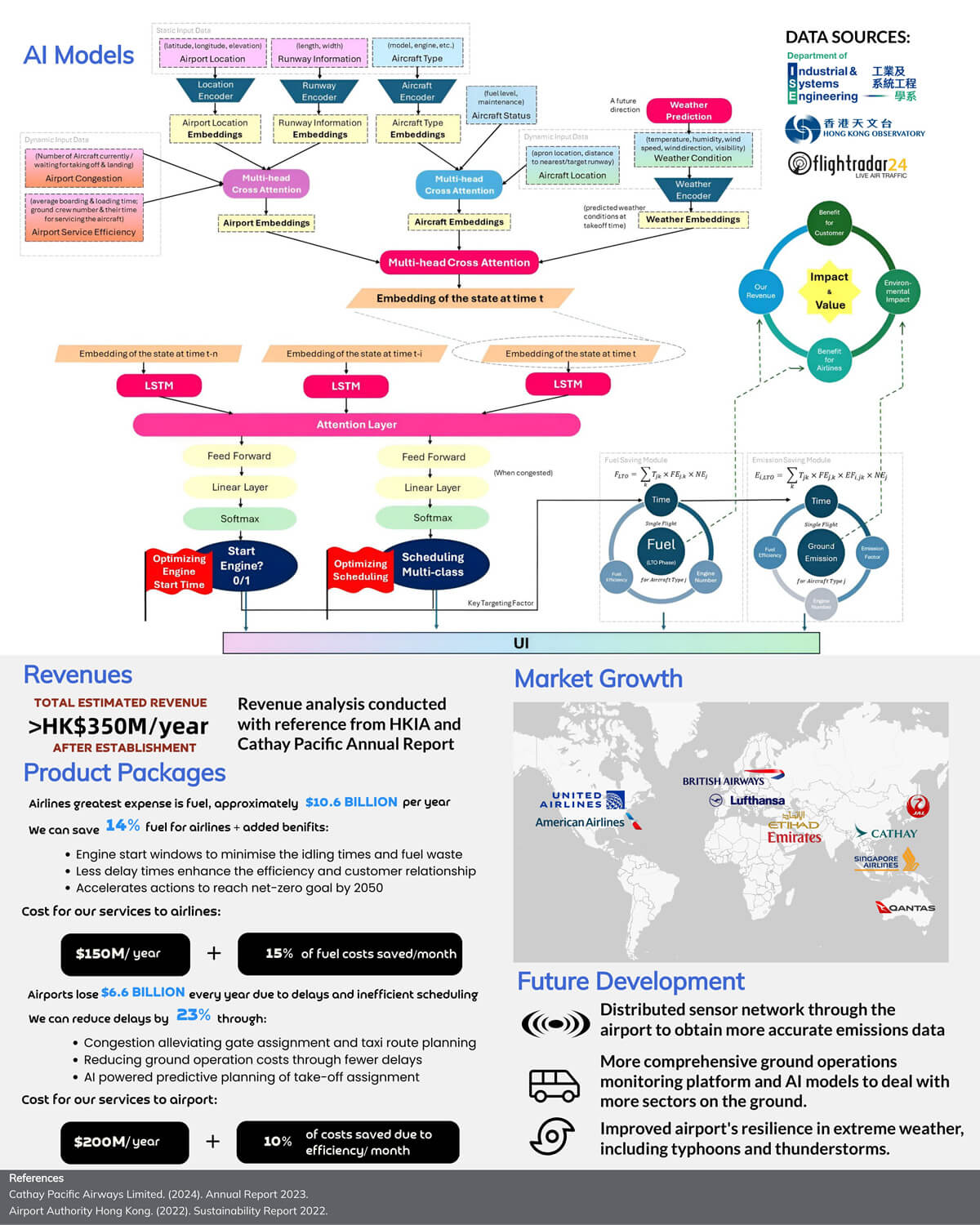
We will develop an innovative AI solution to reduce carbon emissions from aircraft ground operations. Aviation accounts for a large share of transport sector pollution, and engines emit substantial greenhouse gases during taxi, takeoff, and landing. Using sensors to capture real-time engine usage and flight schedules, our system trains a predictive model on how operational factors like pushback timing, taxi routes, and takeoff weight affect emissions output. This model then identifies strategic recommendations tailored for each airport and airline to minimize pollution through optimized engine start windows, efficient runway sequencing, and congestion-alleviating gate assignments that shorten taxi distances. Our automated solution assigns boarding gates and designs taxi routes leveraging its emission predictions. By facilitating intelligent, emissions-conscious ground movement planning through our data-driven approach, we aim to help the aviation industry significantly lower its environmental impact through airport resource utilization.


Presentation
Student Team Members
| Name | Study Program | Study Year |
| CHEN Wai Yan Grace | School of Engineering, Artificial Intelligent | 1 |
| CHI Ting Hsuan | Computer Science and Electronic Engineering | 3 |
| TAM Siu Ho | Electronic Engineering, minor in Information Technology | 2 |
| TANG Justin Kit Hang | World Bachelor in Business | 2 |
| TANG Lok Hang | School of Engineering | 1 |
| WONG Wing Him | Electronic Engineering | 3 |
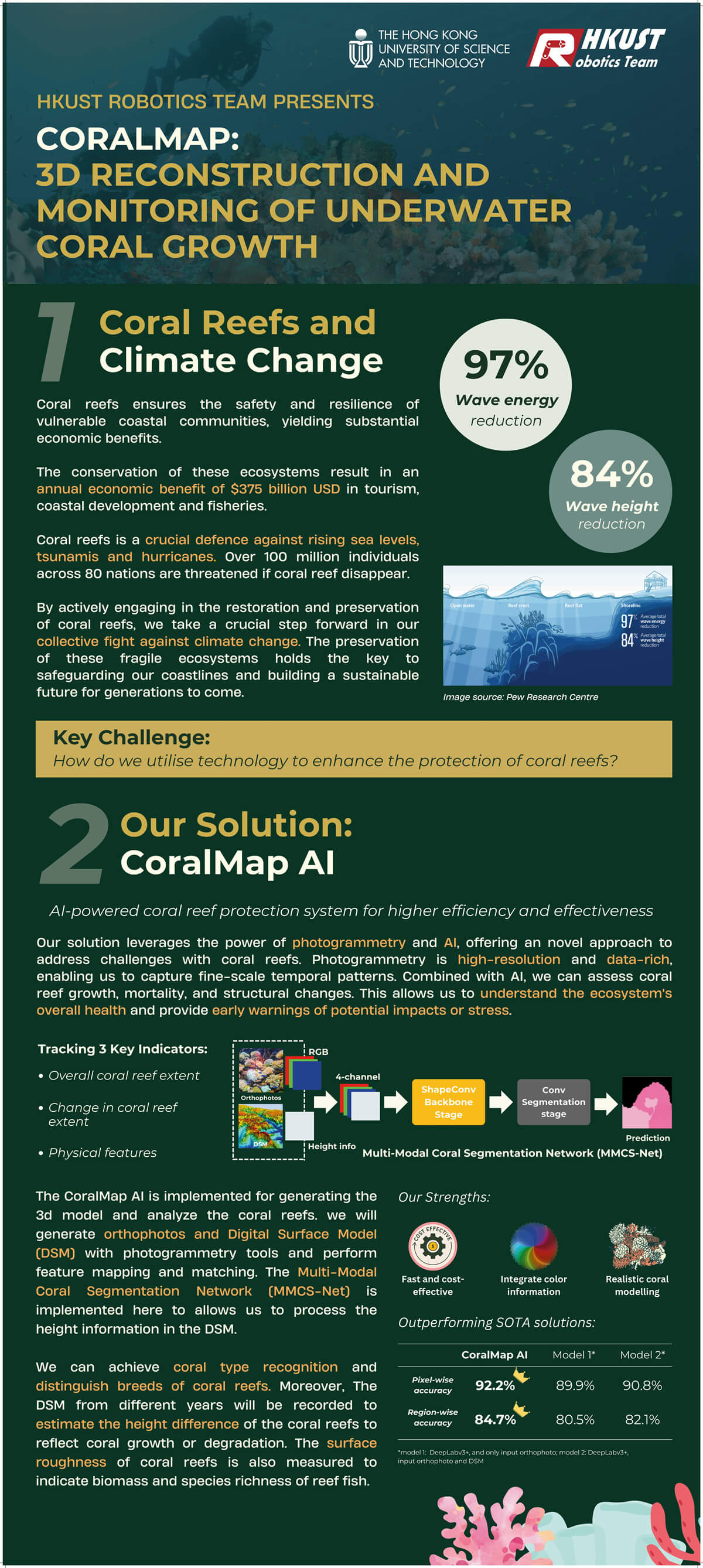
AI-based Photogrammetry for 3D Reconstruction and
Monitoring of Underwater Coral Growth



Presentation
Student Team Members
| Name | Study Program | Study Year |
| Jose Alberto Espino PITTI | Computer Engineering | 3 |
| En Yu YAP | Chemistry | 3 |
| Patt PHURTIVILAI | Computer Science, minor in statistics | 2 |
| Abraham CHANDAFA | Computer Science, minor in Electrical and Electronics Engineering | 2 |
| Cheuk Lam TSANG | Chemistry | 2 |
| Hanyi XIONG | Applied AI | 1 |
FarmGPT: Securing Food Production in the face of
Climate Change with Approachable AI
To address these issues, we propose FarmGPT, an AI-based solution for farmers. Our project involves fine-tuning a chatbot with two types of information. Firstly, we utilize farming-related data, such as AFCD reports, to ensure the model provides accurate information. Secondly, we input farm-specific information obtained through sensors and cameras to generate tailored recommendations that minimize the impact of these challenges.
FarmGPT has a twofold impact.
Firstly, it empowers farmers by providing dynamic AI analysis of their farmland, bridging the technology gap through conversational and digestible information.
Secondly, it enables precision agriculture, allowing farmers to scale their operations while adapting to specific land needs. This approach reduces the reliance on destructive practices like tilling and nitrogen fertilizers, which contribute to climate change. By embracing precision agriculture, farmers can better adapt to the changing environment caused by climate change and mitigate its effects.


